ID Doc centralizes the capture, verification, and data extraction from identity documents (passports, ID cards, driver's licenses, etc.).
The process is a secure and straightforward identity document verification through AI-powered extraction and automated processing of document information.
This page describes its capabilities. Further details will be added later.

Coverage
Documents processed by Namirial AI (by country).
All other documents are handled by our standard reading capability system (see info below).
| Austria ID_CARD_AUT_2010 ID_CARD_AUT_2021 PASSPORT_AUT DRIVER_LICENSE_AUT_2006 DRIVER_LICENSE_AUT_2013_2014 RESIDENCE_PERMIT_AUT_2020 | France ID_CARD_FRA_1994 ID_CARD_FRA_2021 RESIDENCE_PERMIT_FRA_2002 RESIDENCE_PERMIT_FRA_2011 RESIDENCE_PERMIT_FRA_2020 DRIVER_LICENSE_FRA_2013 PASSPORT_FRA | Germany ID_CARD_DEU_2010 ID_CARD_DEU_2021 PASSPORT_DEU_2007 PASSPORT_DEU_2017 RESIDENCE_PERMIT_DEU_2019 | Hungary ID_CARD_HUN_2021 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Italy ITA_TS_CNSTSanitaria ID_CARD_ITA_2016 ID_CARD_ITA_2022 DRIVER_LICENSE_ITA_2013 PASSPORT_ITA_2010 | Romania ID_CARD_ROU_2001 PASSPORT_ROU_2019 | Spain ID_CARD_ESP_2006 ID_CARD_ESP_2015 ID_CARD_ESP_2021 PASSPORT_ESP_2015 | Algeria PASSPORT_DZA NEW |
Extended coverage via our standard reading capability system
For all other countries and document types, ID Doc leverages our standard reading capability system for document identification, data extraction and authenticity checks. With this component We can manage a large number of identity documents worldwide.
Please check with your Namirial technical contact to check the support of the specific use-case ID documents subset.
Official EU sample documents (PRADO)
Browse examples and security features of European identity documents on the Council of the EU's PRADO website.
This solution is based on in-house technologies for image quality control, data extraction and image analysis, as well as connectors to external repositories.
Artificial intelligence technologies such as neural networks, machine learning and deep learning have been developed to guarantee the best possible results given the scanning source (scanner, smartphone, etc.).
The checks answer the following questions:
- Is the image of the document of sufficient quality to be used?
- Is the document what you expected?
- Is the information in the document consistent with the information I have and want to retrieve?
- Is the document authentic?
- Image quality: verify that transmitted images meet minimum quality thresholds.
- Document expectation: verify that the submitted supporting documents match the expected ones.
- Data consistency: compare extracted data from documents with reference information (e.g., customer file).
- Authenticity analysis: analyze the genuineness of the submitted documents.
Automatic analyses of document type and data extraction require a high-contrast, sharp, well-resolved image. These quality requirements are higher than those needed for a human to proofread text. This solution manages its own quality thresholds to optimize the resulting analysis.
Before analyzing the type of document and its content, a check is carried out on the size and resolution. Images that are too small or too large are rejected (see the limits below). The image type is checked: on identity documents, "binary" images (two-color pixels, where all pixels are either black or white) are rejected.
The image must be sufficiently sharp and contrasted. For text documents, a more detailed analysis of text quality is carried out before OCR. Text should be black on a light background, and characters should be large enough to be easily recognized. Exact limits depend on the document type; they are typically around 20 pixels in character height.
Note: on PDF files, only the first two pages are examined to determine whether the first page is blank. In this case, the second page will be processed if it corresponds to a receipt.
| Controlled element | Authorized limits/values |
|---|---|
| File MIME type | PDF, JPEG or PNG. |
| File size | > 0 bytes and < 10 MB. |
| Image size | Width ≥ 320 px and height ≥ 256 px; resolution < 20 MP. |
| Image sharpness | Internal threshold. |
| Image contrast | Internal threshold. |
| Image colorimetry | For identity documents: color or greyscale; not binary. |
| Text size in image | Large enough for OCR; typically ~20 px character height (document-dependent). |
| Analysis of PDF file metadata Note: This check applies to all PDFs supplied. | PDF annotations PDF annotations are checked. These annotations may be the result of a fraudulent attempt to modify certain information in the document. | Modification mark A check is performed to determine whether the text in a document has been modified using Adobe's TouchUp tool. |
|---|
Note: these checks apply to all documents except identity documents.
- Keywords: determine the type of document by searching for keywords (e.g., "balance sheet") and check consistency with expected info (company name, client name, address).
- White list of keywords: absence of keywords in a whitelist can be checked (exact match). For example, "BAS" is not considered found in "AMBASSADE".
- Black list of keywords: presence of forbidden keywords can be checked (exact match). For example, "BAS" is not considered found in "AMBASSADE".
All templates share the same structure, which includes quality control, compliance checks, optional consistency with reference data, authenticity checks, and data extraction with limitations.
All supported documentsReference
https://namirial.atlassian.net/wiki/x/hIDxIw
Context
Fraud has become a sophisticated and borderless threat. As businesses expand, fraudsters broaden their scope, capitalizing on emerging vulnerabilities. This "democratization of fraud" is driven by fraud‑as‑a‑service platforms, AI tools, and other resources that make fraud more accessible—even to non‑experts.
Advances in technology have lowered barriers to entry, removing the need for specialized skills. Pre‑packaged tools make fraudulent activity affordable and easy to execute. At the same time, fraudsters organize in networks and run coordinated schemes (e.g., money muling), which increases the scale and complexity, making detection harder.
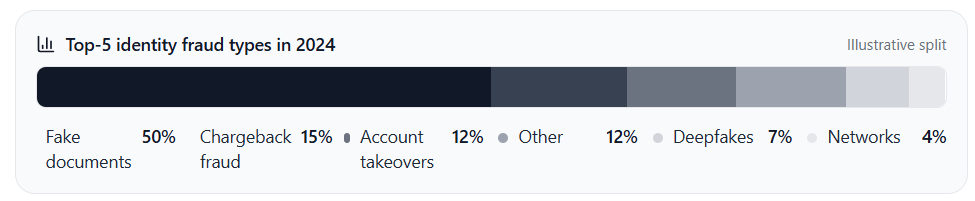
Fake document fraud types Dominant
- Among fake documents, ID cards are the most affected (~70% of fraudulent cases; passports ~13%).
- Forged IDs, passports, and proof‑of‑address remain the top identity fraud vector (~50% of attempts in 2024).
- Dominance is driven by reliance on document checks and the wide availability of forgery tools.
Deepfake fraud types
Deepfakes—AI‑manipulated images, videos, or voices—have surged and now account for a meaningful share of global attempts. They are increasingly used in misinformation and financially motivated scams, and have been implicated in high‑value corporate losses.
| Fighting Fake Document Fraud Advanced document verification: AI‑driven detection of altered fonts, photos, 2D features and holograms. Cross‑document consistency: verify names, dates, photos, numbers and MRZ alignment across sides and sources. Biometric authentication: face match + liveness to bind the user to the document. Real-time data cross-referencing: verify against trusted third-party data and sanctions/watchlists. Expert manual review: trained analysts catch subtle forgeries and decide on escalations. | Fighting Deepfake Fraud AI deepfake detection: models analyze visual/audio artifacts, metadata and digital fingerprints. Real‑time verification: challenge‑based liveness and biometric checks on the capture stream. Risk orchestration: combine device, network and behavioral signals to throttle risky flows. Human‑in‑the‑loop: targeted secondary review for suspicious captures before finalization. |
|---|